Wilson's disease
| Wilson's disease | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Wilson disease, hepatolenticular degeneration |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Field | Endocrinology |
| Symptoms | Swelling of the legs, yellowish skin, personality changes |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Age 5 to 35 |
| Duration | |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | |
| Differential diagnosis | Chronic liver disease, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, others |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Dietary changes, chelating agents, zinc supplements, liver transplant |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | ~1 per 30,000 |
| Deaths | |






Wilson's disease, an autosomal recessive genetic disorder, is characterized by an abnormal accumulation of copper within the body. Copper deposition primarily occurs in the liver and brain, leading to a variety of symptoms. While the condition typically manifests symptoms related to liver and brain function, individuals may exhibit a spectrum of clinical presentations due to the systemic nature of copper distribution.
Clinical Presentation[edit]
Liver-related symptoms often serve as early signs of Wilson's disease and may include vomiting, weakness, abdominal fluid accumulation (ascites), leg swelling (edema), jaundice, and pruritus. Neurological and psychiatric symptoms often appear later and are sometimes the only symptoms in adults. These may include tremors, rigidity, dysarthria, personality changes, anxiety, and hallucinations. The disease's clinical heterogeneity often leads to challenges in its diagnosis, particularly in those with predominantly psychiatric symptoms.
Genetic Basis[edit]
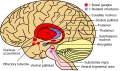
The root cause of Wilson's disease is a mutation in the ATP7B gene, responsible for encoding the Wilson disease protein. This protein plays a critical role in regulating cellular copper transport. Given the autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance, an individual must receive a defective copy of the ATP7B gene from each parent to manifest the disease.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosing Wilson's disease can be challenging due to its varied presentations and the need for a high degree of clinical suspicion. The diagnostic process often involves a combination of blood tests (measuring ceruloplasmin levels and serum copper), 24-hour urine copper tests, and liver biopsy for hepatic copper content. Genetic testing could help in confirming the diagnosis and screening at-risk family members.
Management[edit]
Management of Wilson's disease involves life-long treatment, mainly focusing on reducing the copper load in the body. This usually involves dietary modification to reduce copper intake, alongside pharmacological therapy. Patients are often advised to avoid foods high in copper, such as shellfish, liver, mushrooms, nuts, and chocolate, and to avoid using copper-containing cookware.
Medications used in the management of Wilson's disease include chelating agents like trientine and D-penicillamine that bind copper, promoting its excretion, and zinc supplements, which inhibit the absorption of copper from the gut. In cases with advanced liver disease, liver transplantation may be indicated, which not only resolves the liver disease but also corrects the copper metabolism defect.
Epidemiology[edit]
Wilson's disease has an estimated prevalence of 1 in 30,000 individuals. Symptoms can begin at any age but typically present between ages 5 and 35. The condition affects both sexes equally. The condition was first described in 1854 by Friedrich Theodor von Frerichs and was later named after Dr. Samuel Wilson, who provided detailed descriptions in 1912.
Gallery[edit]
-
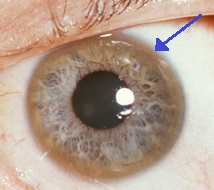
Kayser-Fleischer ring
-
Kayser-Fleischer ring
-
Basal ganglia and related structures
-
Ceruloplasmin protein
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
See also[edit]
|
|
|
| Inborn error of metal metabolism (E83, 275) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Diseases of the nervous system, primarily CNS (G04–G47, 323–349) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Genetic disorder, membrane: ATPase disorders | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
see also ATPase
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian