Syringomyelia

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Syringomyelia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Pain, muscle weakness, stiffness, headache, loss of sensation |
| Complications | Paralysis, scoliosis, chronic pain |
| Onset | Typically adulthood |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Chiari malformation, spinal cord injury, tumors |
| Risks | Congenital conditions, trauma |
| Diagnosis | MRI |
| Differential diagnosis | Multiple sclerosis, spinal cord tumor, transverse myelitis |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgery, physical therapy, pain management |
| Medication | Analgesics, muscle relaxants |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | 8.4 per 100,000 people |
| Deaths | Rarely directly fatal |
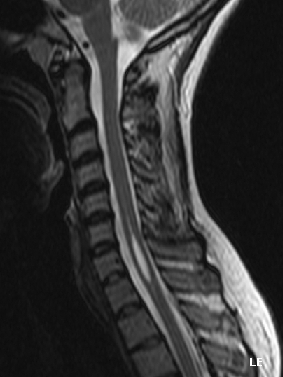
.

Syringomyelia is a neurological disorder characterized by the formation of a cyst or cavity, termed a syrinx, within the spinal cord. Over time, this cyst can expand, damaging the spinal cord and leading to various neurological symptoms. The condition's effects vary depending on the syrinx's location and size within the spinal cord.
Epidemiology[edit]
Approximately 8.4 in every 100,000 individuals are affected by syringomyelia. Symptoms predominantly emerge in young adulthood and typically evolve slowly, although sudden onset can be triggered by actions like coughing, straining, or myelopathy.
Signs and Symptoms[edit]
The symptomatology of syringomyelia is multifaceted and influenced by the syrinx's position within the spinal cord:
- Neuropathic Symptoms: Including chronic pain, sensory abnormalities, and sensation loss, especially in the hands.
- Motor Symptoms: Ranging from temporary weakness to paralysis.
- Autonomic Dysfunction: Manifesting as abnormal body temperature, irregular sweating, bowel control issues, and other related symptoms.
- Syringobulbia: When the syrinx affects the brainstem, it can lead to vocal cord paralysis, ipsilateral tongue atrophy, trigeminal nerve sensory loss, and more.
- Neuropathic Arthropathy: Also known as Charcot joint, it primarily affects the shoulders due to sensory fiber loss to the joint, leading to joint degeneration.
Etiology[edit]
Syringomyelia can be categorized into two primary forms: congenital and acquired. Congenital Syringomyelia: Most commonly linked to Arnold–Chiari malformation or Chiari Malformation. Triggered by anatomical abnormalities like a small posterior fossa, which makes the cerebellum protrude into the cervical region. Can be familial, though this is infrequent. Acquired Syringomyelia: Arises as a complication of various conditions such as trauma, meningitis, tumors, hemorrhage, or arachnoiditis. Post-traumatic syringomyelia (PTS) is a subtype, where symptoms develop after an injury, like a car accident.
Pathogenesis[edit]
The exact pathogenesis of syringomyelia remains a topic of debate. Factors like cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) obstructions in the subarachnoid space, spinal arachnoiditis, Chiari malformation, and spinal vertebrae misalignment have been identified as potential contributors. The source of syrinx fluid, whether from cerebrospinal fluid or blood fluids, is still under investigation.
Diagnosis[edit]
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the principal diagnostic tool for syringomyelia, providing detailed images of the spinal cord and any present syrinx. Additional tests can include: Electromyography (EMG): Assessing potential lower motor neuron damage. Computed Axial Tomography (CT) Scans: Can reveal tumors or hydrocephalus. Myelogram: Rarely used now due to MRI, but it involves radiographs after injecting a contrast medium into the subarachnoid space.
Treatment[edit]
Surgical Interventions:
- Surgery aims to correct the underlying cause of the syrinx.
- In cases with an Arnold-Chiari malformation, the goal is to increase space for the cerebellum.
- Tumor-induced syringomyelia mandates tumor removal.
- Shunting, a procedure to drain the syrinx, may be required. This involves placing a shunt in the syrinx and draining the cerebrospinal fluid, commonly into the abdomen.
- Surgery risks include spinal cord injury, infection, hemorrhage, shunt blockage, and recurrence of syringomyelia.
Non-Surgical Treatments:
- Analgesia is the primary treatment for many patients.
- Medications targeting neuropathic pain, such as gabapentin or pregabalin, are preferred.
- Opiates may be administered for pain management.
- Radiation has limited efficacy and is typically reserved for cases with tumors.
- Syringomyelia at NINDS
|
|
|
| Diseases of the nervous system, primarily CNS (G04–G47, 323–349) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Congenital malformations and deformations of nervous system | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian


