Generalized trichoepithelioma
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Generalized trichoepithelioma | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Multiple familial trichoepithelioma |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| Symptoms | Multiple small skin-colored papules |
| Complications | Basal cell carcinoma |
| Onset | Childhood or adolescence |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic mutation |
| Risks | Family history |
| Diagnosis | Skin biopsy, Genetic testing |
| Differential diagnosis | Basal cell carcinoma, Syringoma, Milia |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgical excision, Laser therapy, Electrodesiccation |
| Medication | Topical retinoids, Oral retinoids |
| Prognosis | Generally benign |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
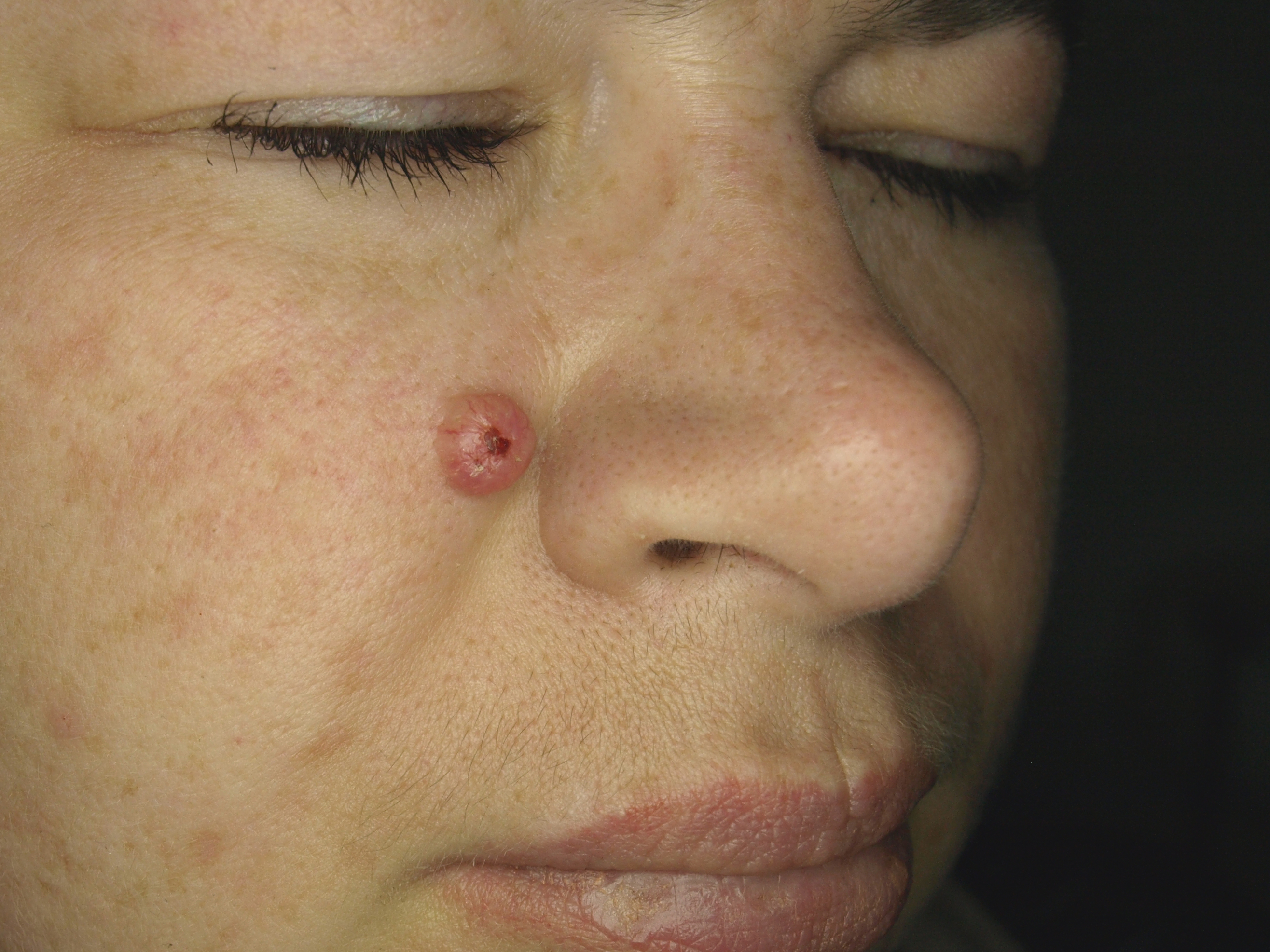
Generalized trichoepithelioma is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the presence of multiple benign skin tumors known as trichoepitheliomas. These tumors originate from the hair follicles and are typically found on the face, scalp, and neck.
Clinical Features
Generalized trichoepithelioma presents with numerous small, firm, skin-colored papules. These papules are usually symmetrically distributed and can coalesce into larger plaques. The condition is often first noticed in childhood or adolescence and tends to progress with age.
Symptoms
- Multiple papules on the face, particularly around the nose, cheeks, and forehead. - Papules may also appear on the scalp, neck, and upper trunk. - Lesions are typically asymptomatic but can occasionally cause itching or irritation.
Pathophysiology
Generalized trichoepithelioma is caused by mutations in the CYLD gene, which is responsible for encoding a protein that regulates cell growth and division. The mutation leads to uncontrolled proliferation of cells in the hair follicle, resulting in tumor formation.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is primarily clinical, based on the characteristic appearance of the lesions. A skin biopsy can be performed to confirm the diagnosis, revealing nests of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading and keratin cysts.
Treatment
There is no definitive cure for generalized trichoepithelioma, but several treatment options can help manage the condition: - Surgical excision: Individual lesions can be removed surgically, although new lesions may develop. - Laser therapy: Carbon dioxide laser or pulsed dye laser can be used to reduce the appearance of lesions. - Topical treatments: Topical retinoids or imiquimod cream may be used to reduce lesion size.
Prognosis
The prognosis for individuals with generalized trichoepithelioma is generally good, as the condition is benign and does not affect overall health. However, the cosmetic appearance of the lesions can be distressing for patients.
See Also
- Trichoepithelioma - Basal cell carcinoma - Skin tumor - Genetic disorder
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD

